langchain - (3) ToolNode
Reference
@tool, llm.bind_tools(), ToolNode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode
@tool
def get_weather(location:str):
"""Call to get the weather"""
if location in ["서울", "인천"]:
return "수도권은 13도이며, 안개가 짙습니다."
else:
return "수도권 외 지역은 15도이며, 화창합니다."
tools = [get_weather]
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)
llm_with_tools = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini").bind_tools(tools)
result_toolcall = llm_with_tools.invoke("부산 날씨는 어때?").tool_calls
위 코드는 크게 아래 2가지를 수행하는 샘플 코드이다.
@tool: 파이썬 함수get_weather를 langchain의tool객체로 변환하고,- langchain
tool객체:langchain_core.tools.StructuredTool(LangchainBaseTool상속) TooldocStructuredTooldoc
- langchain
ChatOpenAI.bind_tools(tools): 앞서 선언한tool을llm이 실행
추가로 langgraph를 구축하는 과정에서 tool을 실행 가능한 하나의 node로 정의하는 과정인 ToolNode 선언 과정도 포함되어 있다.
ToolNode: 선언된tool객체를 langgraphNode로 정의
ToolNode
ToolNode 는 어떤 역할을 할까?
간단히 말하면 Tool을 langgraph의 Node객체로 변환하는 역할을 한다. langgraph에서는 특정한 함수, 객체는 Node로 정의되고, 이를 Edge로셔 연결해준다. 그래서 graph구조로 정의해 다양한 시나리오와 passage에 맞춰 유연한 LLM application structure를 구성할 수 있게 되는 것이다.
다양한 시나리오에 맞게 적합한 함수(Tool)를 활용하는 것은 이 컨셉에 매우 중요하며, 이를 위해 정의되는 것이 바로 ToolNode이다.
ToolNode의 역할을 심플한 하나의 사례를 통해 살펴보자.
이를 위해 langgraph를 사용해 ToolNode가 포함된 graph 시나리오를 정의한다.
우선 Graph의 Node간 전달할 정보를 State로 정의한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# State 설정
from typing import TypedDict, Annotated
from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages
class State(TypedDict):
"""
message 주고 받는 state 설정
"""
messages: Annotated[list, add_messages]
그리고 tool을 정의한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# tool 정의
from langchain_core.tools import tool
@tool
def get_weather(location:str):
"""Call to get the weather"""
if location in ["서울", "인천"]:
return "수도권은 13도이며, 안개가 짙습니다."
else:
return "수도권 외 지역은 15도이며, 화창합니다."
다음으로 Node를 정의한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# Node 정의
## tool node 정의
from langgraph.prebuilt import ToolNode, tools_condition
tools=[get_weather]
tool_node = ToolNode(tools)
## chatbot node 정의
### llm tool binding
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
llm_with_tools = llm.bind_tools(tools)
### chatbot node 정의
def simple_chat(state: State):
response = llm_with_tools.invoke(state['messages'])
return {"messages": [response]}
마지막으로 graph를 정의한다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph
graph_builder = StateGraph(State)
graph_builder.add_node("tools", tool_node)
graph_builder.add_node("chatbot", simple_chat)
graph_builder.set_entry_point("chatbot")
graph_builder.add_edge("tools", "chatbot")
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("chatbot", tools_condition)
graph = graph_builder.compile()
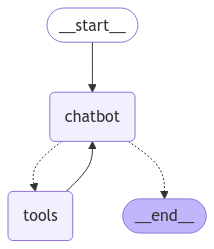
이렇게 생성한 graph를 Image 패키지릃 사용해 시각화 하면 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
### 그래프 시각화
from IPython.display import Image, display
img = Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())
with open("output_toolnode.png", "wb") as f:
f.write(img.data)
chatbot 노드는 tool 사용 여부를 결정해 tools_condition이라는 conditional_edge 구조를 바탕으로 ToolNode(tools)와 interaction을 수행하는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
tools_condtion라우팅과 ToolNode 의 역할
ToolNode는 LLM의 tool_calling 정보를 받아
tool을 실행하고- 그 결과를
ToolMessage객체로 담아 response를 한다.
이렇게 제작된 ToolMessage는 다시 chatbot노드에 전달돼 최종 LLM 메시지(AI Message)가 생성된다.
이를 구조화해 그려보면 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
A: State (messages)
└── B: Chatbot Node
├── (1) LLM 호출 (ChatOpenAI)
│ └── Last Message 생성 *LLM이 tool 사용이 필요한 지 여부도 판단. 필요할 경우 tool_calls 정보를 생성해 response.
│ ├── tool_calls 포함된 경우
│ └── tool_calls 없는 경우
│
├── (2) tools_condition 라우팅
│ ├── i) tool_calls 있음 → "tools"
│ │ └── ToolNode
│ │ ├── a) Tool 실행 (get_weather 등)
│ │ │ ├── tool 이름
│ │ │ ├── arguments
│ │ │ └── call_id 파싱
│ │ │
│ │ └── b) ToolMessage 객체 반환
│ │ ├── content (실행 결과)
│ │ ├── tool_call_id
│ │ └── name
│ │ └── State messages에 추가
│ │
│ └── ii) tool_calls 없음 → "__end__"
│
└── 반복: ToolMessage가 있으면 다시 Chatbot Node로
tool_calling을 하는 경우
최종적으로 이 graph에 대해 invoke를 수행하면 아래와 같은 결과를 확인할 수 있다. HumanMessage > AIMessage > ToolMessage > AIMessage 의 순서로 생성되고, 예상되로 tool_calling을 수행하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
res_node = graph.invoke({"messages": {"role": "user", "content": "지금 수도권 날씨는 어때?"}})
res_node
>> {
'messages': [
HumanMessage(content='지금 수도권 날씨는 어때?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='1196e1be-6e73-4a15-bbc0-f6958830d380'),
AIMessage(content='', additional_kwargs={'tool_calls': [{'id': 'call_k4PkKV0y1qXfcjv2JkXrzAan', 'function': {'arguments': '{"location":"수도권"}', 'name': 'get_weather'}, 'type': 'function'}], 'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 17, 'prompt_tokens': 53, 'total_tokens': 70, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_bd83329f63', 'finish_reason': 'tool_calls', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-766a3b1b-f376-4304-a6c0-74a036cff0e3-0', tool_calls=[{'name': 'get_weather', 'args': {'location': '수도권'}, 'id': 'call_k4PkKV0y1qXfcjv2JkXrzAan', 'type': 'tool_call'}], usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 53, 'output_tokens': 17, 'total_tokens': 70, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}}),
ToolMessage(content='수도권 외 지역은 15도이며, 화창합니다.', name='get_weather', id='a6f84c8d-b11a-46b5-aa2a-fdcdec3f165a', tool_call_id='call_k4PkKV0y1qXfcjv2JkXrzAan'),
AIMessage(content='현재 수도권의 날씨는 15도이며, 화창한 상태입니다.', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 20, 'prompt_tokens': 92, 'total_tokens': 112, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_72ed7ab54c', 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-3e041afc-4d88-4e62-b468-0d7be1c98cee-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 92, 'output_tokens': 20, 'total_tokens': 112, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}}
)
]
}
이를 바탕으로 아래와 같은 구조로 tool_calling이 이루어졌을 것을 추론할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
A: State messages의 timeline 분석
└── 1. User Input (HumanMessage)
│ content: "지금 수도권 날씨는 어때?"
│
└── 2. LLM의 첫 응답 (AIMessage with tool_calls)
│ content: "" (비어있음)
│ tool_calls 정보:
│ ├── id: "call_k4PkKV0y1qXfcjv2JkXrzAan"
│ ├── name: "get_weather"
│ └── arguments: {"location":"수도권"}
│
└── 3. Tool 실행 결과 (ToolMessage)
│ content: "수도권 외 지역은 15도이며, 화창합니다."
│ name: "get_weather"
│ tool_call_id: "call_k4PkKV0y1qXfcjv2JkXrzAan"
│
└── 4. LLM의 최종 응답 (AIMessage)
│ content: "현재 수도권의 날씨는 15도이며, 화창한 상태입니다."
│ finish_reason: "stop" (더 이상의 tool_calls 없음)
tool_calling을 하지 않는 경우
tool_calling을 하지 않을 경우의 결과는 아래와 같다. HumanMessage > AIMessage의 순서로 생성되고, tool_calling을 수행하지 않고 ToolMessage도 생성하지 않는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
res = graph.invoke({"messages": {"role": "user", "content": "마이크로소프트가 어떤 회사야?"}})
res['messages']
>> [
HumanMessage(content='마이크로소프트가 어떤 회사야?', additional_kwargs={}, response_metadata={}, id='7cee9f62-7182-42f8-b18b-d9acda33a409'),
AIMessage(content='마이크로소프트(Microsoft)는 미국의 다국적 기술 기업으로, 주로 소프트웨어, 소비자 전자제품, 개인용 컴퓨터 및 서비스 분야에서 활동하고 있습니다. 1975년에 빌 게이츠(Bill Gates)와 폴 앨런(Paul Allen)에 의해 설립되었습니다. 마이크로소프트의 대표적인 제품으로는 운영 체제인 윈도우(Windows), 오피스 생산성 소프트웨어(Office Suite), 클라우드 서비스인 애저(Azure) 등이 있습니다.\n\n또한, 마이크로소프트는 게임 산업에도 진출하여 인기 게임 콘솔인 Xbox를 운영하고 있습니다. 이 외에도 AI, 디지털 비즈니스 솔루션, 핀테크 등 다양한 분야에 걸쳐 연구 및 개발을 진행하고 있습니다.\n\n마이크로소프트는 글로벌 시장에서 큰 영향력을 가지고 있으며, 기술 혁신과 기업용 솔루션 제공에 주력하고 있습니다.', additional_kwargs={'refusal': None}, response_metadata={'token_usage': {'completion_tokens': 207, 'prompt_tokens': 53, 'total_tokens': 260, 'completion_tokens_details': {'accepted_prediction_tokens': 0, 'audio_tokens': 0, 'reasoning_tokens': 0, 'rejected_prediction_tokens': 0}, 'prompt_tokens_details': {'audio_tokens': 0, 'cached_tokens': 0}}, 'model_name': 'gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', 'system_fingerprint': 'fp_72ed7ab54c', 'finish_reason': 'stop', 'logprobs': None}, id='run-a730d6b3-27e0-4065-a85a-5c96b6423655-0', usage_metadata={'input_tokens': 53, 'output_tokens': 207, 'total_tokens': 260, 'input_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'cache_read': 0}, 'output_token_details': {'audio': 0, 'reasoning': 0}})
]
구조를 그려보면 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
A: State messages의 timeline 분석 (Tool 미사용 케이스)
└── 1. User Input (HumanMessage)
│ content: "마이크로소프트가 어떤 회사야?"
│
└── 2. LLM의 응답 (AIMessage)
│ content: 직접 응답 생성 (tool_calls 없음)
│ finish_reason: "stop"
│ metadata:
├── tokens: 총 260개
│ ├── input: 53
│ └── output: 207
└── model: gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18
tools_condition
1
2
3
from langgraph.prebuilt import tools_condition
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("chatbot", tools_condition)
위 코드에서 tools_condition은 아래와 같이 tools(ToolNode)로 갈 것인지, END로 갈 것인지 분기하는 심플한 함수이다. tools로 갈 지의 여부는 last message가 tool_calls라는 attribute를 갖고 있는 지 여부로 판단한다. LLM이 인지 추론으로 tool로 갈지를 결정하는 게 아니라, 이미 LLM이 앞서 결정해 뱉은 response를 기준으로 심플하게 tool로 보내거나 하는 거수기 역할 같은 것이다.
1
2
3
4
def tools_condition(
state: Union[list[AnyMessage], dict[str, Any], BaseModel],
messages_key: str = "messages",
) -> Literal["tools", "__end__"]:
LLM은 tool을 사용해야 한다는 판단을 했다면 last message가 tool_calls 정보를 담고있었을 것이고, tools_condition은 이 경우, llm이 필요하다고 판단한(호출한, “calls”) tool function을 Toolnode로 연결하는 역할을 한다(return "tools"). ToolMessage 객체로 담아 다시 Chatbot에게 전달하는 ToolNode로 연결한다.