langgraph - Memory, Multi-vector Indexing
langgraph Memory Store
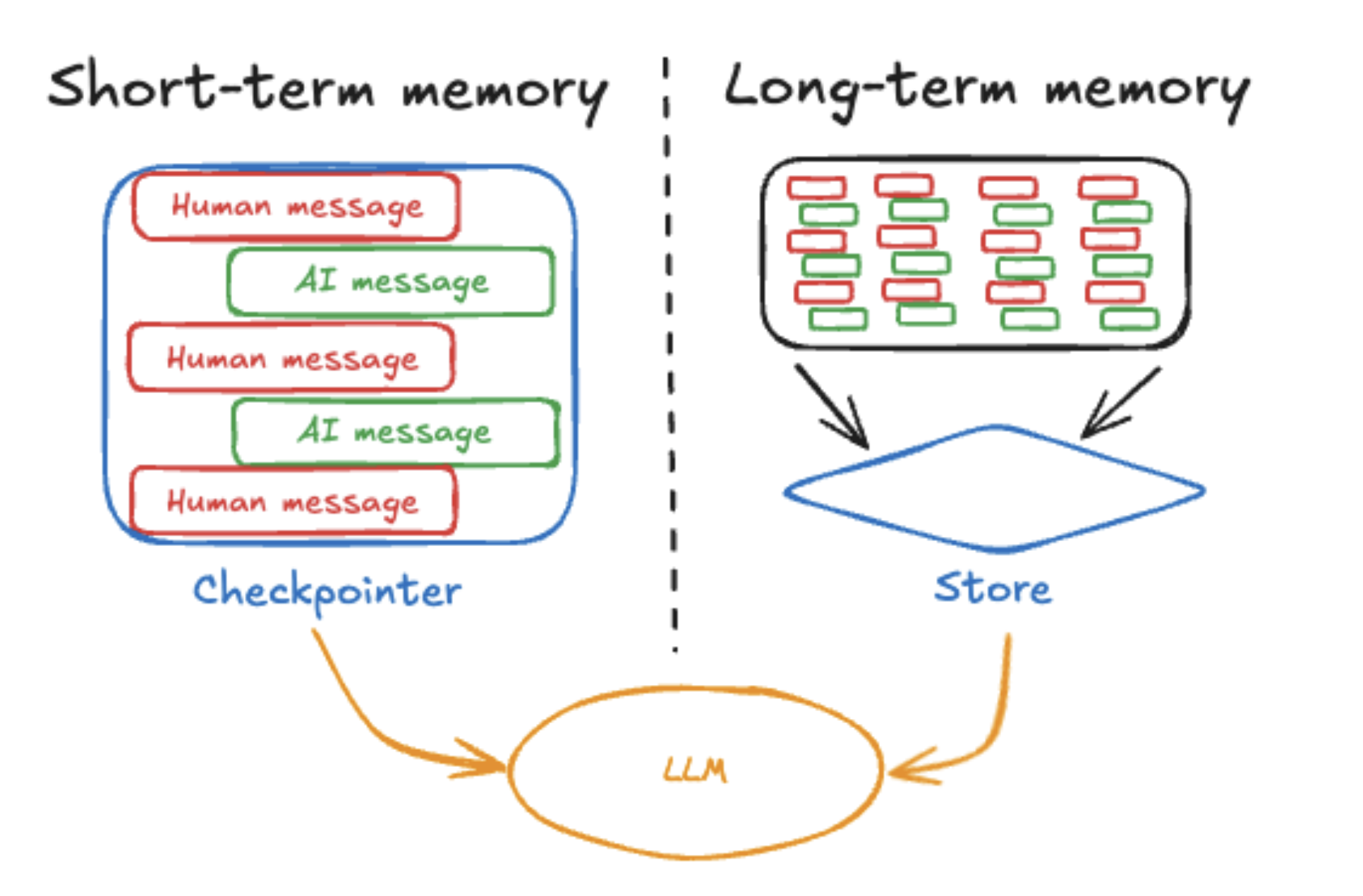
langgraph는 단기 memory와 장기 memory를 구분해 접근합니다.
단기 memory는 앞서 살펴본 것과 같이 주로 checkpoint를 활용합니다.
장기 memory는 Store라는 객체를 활용합니다.
그리고 이 Store에는 Semantic Search를 가능하게 하는 Vector indexing도 가능합니다. 이번 글에서는 multi-vector indexing을 통해 여러 종류의 정보를 동시에 검색할 수 있는 방법에 대해 살펴보겠습니다. 이를 통해 예를 들어, “콘텐츠”와 “감정 상태” 같은 서로 다른 속성을 동시에 인덱싱하고, 필요에 따라 특정 속성만을 검색에 활용하도록 할 수 있습니다.
아울러, Store.put, Store.search, Store.get 메서드에 대한 간단한 설명도 함께 살펴보겠습니다.
Multi-Vector Indexing 기본 개념
langgraph에서 multi-vector indexing은 하나의 데이터(여기서는 하나의 메모리)에 대해 여러 필드를 각각 임베딩하여 저장해두고, 검색 시점에 원하는 필드만을 대상으로 유사도 검색을 수행할 수 있도록 하는 기술입니다.
예를 들어,
memory필드에는 사건(혹은 기억) 자체를,emotional_context필드에는 해당 사건에서의 감정 상태
를 인덱싱해둔다면, 검색할 때 “행복했던 순간” 같은 감정 키워드를 위주로 찾을 수도 있고, “피자 먹은 추억”처럼 사건 위주로 찾을 수도 있습니다.
아래 예시에서는 InMemoryStore를 활용해 memory와 emotional_context 두 필드를 모두 인덱싱하도록 설정하겠습니다.
Multi-Vector Indexing 예시
코드 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
from langgraph.store.memory import InMemoryStore
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# Embeddings 함수 (실제로는 OpenAIEmbeddings 등을 사용)
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(model="text-embedding-ada-002")
# InMemoryStore를 multi-vector로 구성하여, "memory"와 "emotional_context" 두 필드를 인덱싱
store = InMemoryStore(
index={"embed": embeddings, "dims": 1536, "fields": ["memory", "emotional_context"]}
)
# 메모리 저장(put): memory와 emotional_context 를 함께 인덱싱
store.put(
("user_123", "memories"),
"mem1",
{
"memory": "Had pizza with friends at Mario's",
"emotional_context": "felt happy and connected",
"this_isnt_indexed": "I prefer ravioli though",
},
)
store.put(
("user_123", "memories"),
"mem2",
{
"memory": "Ate alone at home",
"emotional_context": "felt a bit lonely",
"this_isnt_indexed": "I like pie",
},
)
# Search: 감정적인 부분을 중점으로 검색
print("=== Search: times they felt isolated ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="times they felt isolated", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Emotion: {r.value['emotional_context']}\n")
# Search: 사회적 활동(피자 먹은) 부분을 중점으로 검색
print("=== Search: fun pizza ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="fun pizza", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Emotion: {r.value['emotional_context']}\n")
# Search: "ravioli"는 인덱스에 포함되지 않음 (this_isnt_indexed 필드이므로)
print("=== Search: ravioli ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="ravioli", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Emotion: {r.value['emotional_context']}\n")
실행 결과
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
=== Search: times they felt isolated ===
Item: mem2; Score (0.5895009051396596)
Memory: Ate alone at home
Emotion: felt a bit lonely
=== Search: fun pizza ===
Item: mem1; Score (0.6207546534134083)
Memory: Had pizza with friends at Mario's
Emotion: felt happy and connected
=== Search: ravioli ===
Item: mem1; Score (0.2686278787315685)
Memory: Had pizza with friends at Mario's
Emotion: felt happy and connected
결과에서 보듯, 감정 상태에 중점을 둔 쿼리(“times they felt isolated”)에서는 mem2가 높은 점수를 받고, 피자 중심의 쿼리(“fun pizza”)에서는 mem1이 높은 점수를 받았습니다. 인덱싱 대상이 아닌 this_isnt_indexed 필드(ravioli 텍스트)는 검색 점수가 낮아지는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
인덱싱 필드 동적 변경 (Override)
기본적으로 InMemoryStore를 생성할 때 지정한 필드(fields)들이 인덱싱에 사용됩니다. 하지만, 특정 데이터를 저장(put)할 때만 인덱싱 필드를 다르게 하고 싶다면 index=["원하는필드들"] 옵션을 줄 수 있습니다.
코드 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
store = InMemoryStore(
index={
"embed": embeddings,
"dims": 1536,
"fields": ["memory"], # 기본적으로 "memory"만 인덱싱
}
)
# mem1: 기본 설정 -> "memory" 필드 인덱싱
store.put(
("user_123", "memories"),
"mem1",
{"memory": "I love spicy food", "context": "At a Thai restaurant"},
)
# mem2: 저장 시점에 "context"만 인덱싱
store.put(
("user_123", "memories"),
"mem2",
{"memory": "I love hot food", "context": "Dinner at an Italian place"},
index=["context"], # 이 item만 context 필드를 인덱싱
)
# Search: 음식 취향 관련 -> mem1 매칭 예상
print("=== Search: what food do they like ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="what food do they like", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Context: {r.value['context']}\n")
# Search: 식당 환경 관련 -> mem2 매칭 예상
print("=== Search: restaurant environment ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="restaurant environment", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Context: {r.value['context']}\n")
실행 결과
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
=== Search: what food do they like ===
Item: mem1; Score (0.3374968677940555)
Memory: I love spicy food
Context: At a Thai restaurant
=== Search: restaurant environment ===
Item: mem2; Score (0.36784461593247436)
Memory: I love hot food
Context: Dinner at an Italian place
특정 데이터 인덱싱 제외 (Disable Indexing)
때로는 내용 검색 대상이 아니지만, 저장은 해야 하는 데이터가 있을 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 시스템 로그나 내부 플래그 같은 데이터가 그러합니다. 이런 경우 index=False로 설정하면 아예 벡터 인덱스에 추가되지 않고, 단순 저장/조회(.get) 등으로만 활용 가능합니다.
코드 예시
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
store = InMemoryStore(
index={"embed": embeddings, "dims": 1536, "fields": ["memory"]}
)
# 검색 대상인 메모리
store.put(
("user_123", "memories"),
"mem1",
{"memory": "I love chocolate ice cream", "type": "preference"},
)
# 검색 대상에서 제외할 메모리
store.put(
("user_123", "memories"),
"mem2",
{"memory": "User completed onboarding", "type": "system"},
index=False # 인덱싱하지 않음
)
# "food preferences"라는 쿼리로 검색 -> mem1이 매칭
print("=== Search: what food preferences ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="what food preferences", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Type: {r.value['type']}\n")
# "onboarding"라는 쿼리로 검색 -> mem2는 인덱싱되어 있지 않으므로 잘 안 뜸
print("=== Search: onboarding status ===")
results = store.search(("user_123", "memories"), query="onboarding status", limit=1)
for r in results:
print(f"Item: {r.key}; Score ({r.score})")
print(f"Memory: {r.value['memory']}")
print(f"Type: {r.value['type']}\n")
실행 결과
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
=== Search: what food preferences ===
Item: mem1; Score (0.32269984224327286)
Memory: I love chocolate ice cream
Type: preference
=== Search: onboarding status ===
Item: mem1; Score (0.010241633698527089)
Memory: I love chocolate ice cream
Type: preference
mem2(“User completed onboarding”)는 검색되지 않고 있습니다. (낮은 점수로 다른 항목이 대신 나옴)
Store 메서드 상세 설명
1. put
1
2
3
4
5
6
put(
namespace: tuple[str, ...],
key: str,
value: dict[str,Any],
index: Optional[Union[Literal[False], list[str]]] = None
)
- 역할: 특정 공간(
namespace) 안에key로 식별되는 데이터를 저장합니다. - 매개변수
namespace: 계층적 경로를 지정하는 튜플. 예)("user_123", "memories")key: 해당 namespace 내에서 유니크한 식별자.value: 실제로 저장할 데이터(딕셔너리 형태).index:None(기본값): Store를 생성할 때 지정한 기본 인덱싱 필드를 그대로 사용False: 인덱싱 안 함list[str]: 해당 아이템을 저장할 때만 인덱싱할 필드(경로) 목록
예시
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
# 기본 인덱싱 store.put(("docs",), "report", {"memory": "Will likes ai"}) # 인덱싱 비활성화 store.put(("docs",), "report", {"memory": "Will likes ai"}, index=False) # 특정 필드만 인덱싱 store.put(("docs",), "report", {"memory": "Will likes ai"}, index=["memory"])
2. search
1
2
3
4
5
6
search(
namespace_prefix: tuple[str, ...],
query: Optional[str] = None,
filter: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None,
limit: int = 10, offset: int = 0
) -> list[SearchItem]
- 역할: 해당
namespace_prefix아래 저장된 데이터들을 조건에 맞게 검색합니다.query가 주어지면 벡터 임베딩(semantic search)을 수행합니다(임베딩 설정이 되어 있는 경우).filter가 주어지면, key-value 형태의 일치 여부로 1차 필터링한 뒤, query가 있다면 2차 벡터 검색을 수행합니다.
- 매개변수
namespace_prefix: 검색 범위를 지정할 튜플. 예)("user_123", "memories")query: 검색하고자 하는 텍스트(semantic search).filter: 단순 속성값 필터(= 조건).limit: 검색 결과 개수 제한.offset: 스킵할 검색 결과 개수.
예시
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
# 단순 필터링 results = store.search( ("docs",), filter={"type": "article", "status": "published"} ) # 벡터 검색 results = store.search( ("docs",), query="machine learning applications in healthcare", filter={"type": "research_paper"}, limit=5 )
3. get
1
2
3
4
get(
namespace: tuple[str, ...],
key: str
) -> Optional[Item]
- 역할:
namespace및key로 단일 아이템을 가져옵니다. - 매개변수
namespace: 저장된 데이터의 계층 경로.key: 유니크 식별자.
예시
1 2 3
item = store.get(("docs",), "report") if item: print(item.value) # 저장된 dict 확인
get은 단순 조회 함수이며, 검색 점수나 벡터 연산 없이 직접 key를 아는 경우에 사용하게 됩니다.
langgraph의 InMemoryStore를 사용해 multi-vector indexing을 적용하면, 하나의 데이터에 대한 여러 다차원적 속성을 자유롭게 검색할 수 있습니다. 예시에서는 memory와 emotional_context를 함께 인덱싱했지만, 실제로는 메타데이터(예: 위치, 태그, 카테고리 등)나 사용자 상태(예: 감정, 의도 등)도 함께 인덱싱해 더욱 풍부한 검색을 구현할 수 있습니다.
- 인덱싱할 필드와 인덱싱을 제외할 필드를 적절히 조합하여, 필요할 때만 특정 속성으로 유사도 검색을 수행
override fields(저장 시점에만 특정 필드 인덱싱) 기능을 활용해, 동적으로 검색 속성을 변경index=False를 통해 시스템 내부용 데이터는 검색 인덱스에서 제외